Geothermal cooling offers you natural, energy-efficient comfort for your home. You can harness the earth's stable underground temperature through techniques like earth tube systems, ground-coupled heat exchangers, and geothermal heat pumps. Earth-sheltered home designs maximize this cooling potential, while passive geothermal methods use underground labyrinths to cool air naturally. Radiant floor cooling and earth-air heat exchangers provide silent, even temperature distribution. For larger projects, geothermal cooling towers and borehole thermal energy storage offer long-term solutions. These innovative approaches can slash your energy consumption by up to 50%, creating a more sustainable and comfortable living environment. Exploring these options further will reveal their full potential for your home.
Earth Tube Cooling Systems
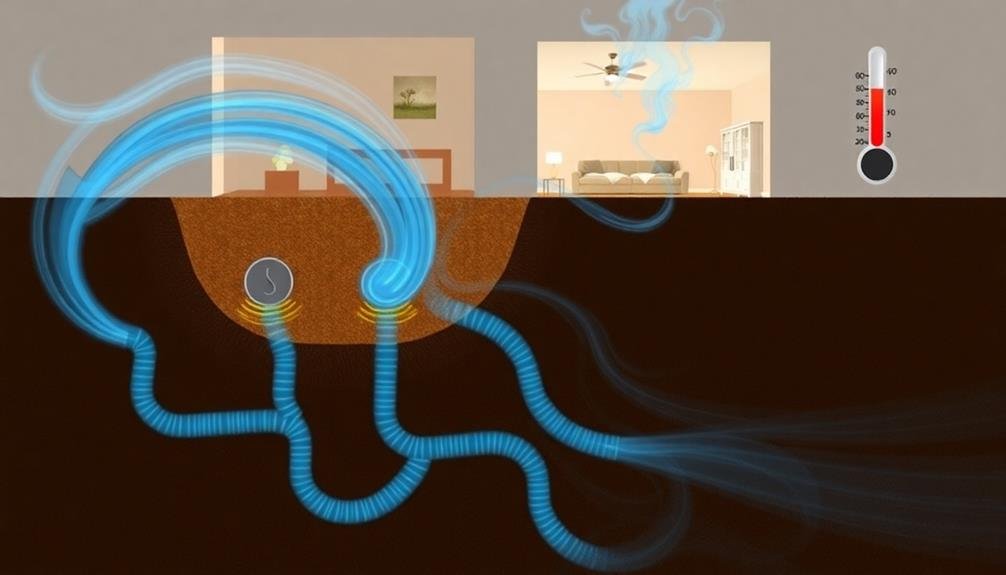
Earth tube cooling systems are among the most efficient geothermal techniques for home cooling. They work by utilizing the constant temperature of the earth below the frost line to cool air before it enters your home.
You'll need to bury large pipes about 6 to 10 feet underground, where temperatures remain stable year-round. As warm outdoor air is drawn through these pipes, it cools down to match the earth's temperature. This cooled air is then circulated into your home, reducing the need for traditional air conditioning.
The system's efficiency increases in areas with significant temperature differences between summer and winter. You'll find that earth tube systems are most effective when combined with proper home insulation and ventilation.
They're particularly useful in climates with hot summers and cool winters. While the initial installation cost can be high, you'll save on energy bills in the long run. Maintenance is minimal, but you'll need to guarantee the pipes remain clean and free from moisture buildup to prevent mold growth.
Consider consulting with a geothermal specialist to determine if an earth tube system is suitable for your home's specific location and climate conditions.
Ground-Coupled Heat Exchangers
Ground-coupled heat exchangers offer another effective geothermal cooling solution for your home. These systems utilize the earth's stable temperature to cool your living space efficiently.
You'll need to install a network of pipes buried in your yard, typically at depths of 6 to 10 feet. As fluid circulates through these pipes, it absorbs the coolness from the ground and transfers it to your home.
The system works by pumping the cooled fluid to a heat exchanger inside your house, where it's used to lower the air temperature. You can integrate this with your existing HVAC system or use it as a standalone cooling method.
Ground-coupled heat exchangers are particularly effective in areas with moderate climates and can greatly reduce your energy consumption.
When considering installation, you'll need to assess your property's soil conditions and available space. The system's efficiency depends on factors like soil composition, moisture content, and local climate.
While the initial investment may be higher than traditional cooling systems, you'll benefit from lower operating costs and a reduced carbon footprint over time.
Remember to consult with a geothermal expert to determine the best configuration for your specific needs.
Passive Geothermal Cooling Design

You can harness passive geothermal cooling through earth-coupled heat exchangers and underground thermal labyrinths.
Earth-coupled heat exchangers use buried pipes to transfer heat between your home and the cooler ground.
Underground thermal labyrinths, on the other hand, create a maze-like network of underground passages that naturally cool air as it circulates through them before entering your living space.
Earth-Coupled Heat Exchangers
A hidden gem in passive geothermal cooling, earth-coupled heat exchangers harness the stable temperatures beneath our feet. These systems circulate air or liquid through underground pipes, taking advantage of the earth's constant temperature to cool your home efficiently.
You'll find earth-coupled heat exchangers in two main forms: air-based and liquid-based systems. Air-based systems, also known as earth tubes, draw fresh air through buried pipes before circulating it into your home. Liquid-based systems use a network of underground pipes filled with water or antifreeze to transfer heat between your home and the earth.
Here's why you should consider earth-coupled heat exchangers:
- Energy-efficient: They reduce your reliance on traditional air conditioning
- Cost-effective: Lower energy bills and minimal maintenance costs
- Environmentally friendly: Decreased carbon footprint compared to conventional cooling
- Versatile: Can be used for both cooling and heating
To implement an earth-coupled heat exchanger, you'll need to assess your property's soil conditions, available space, and local regulations.
While the initial installation cost may be higher than traditional systems, the long-term energy savings and environmental benefits make it a worthwhile investment for many homeowners.
Underground Thermal Labyrinth
For centuries, architects have drawn inspiration from nature's cooling mechanisms. An underground thermal labyrinth is a passive geothermal cooling technique that mimics the natural cooling processes found in cave systems. You can incorporate this design into your home by creating a network of underground passages beneath or adjacent to your living space.
The labyrinth works by drawing warm air from your home through these cooler underground channels. As the air travels through the passages, it loses heat to the surrounding earth, which maintains a consistent temperature year-round. The cooled air then re-enters your home, reducing the need for mechanical cooling systems.
To implement an underground thermal labyrinth effectively, consider these key factors:
| Design Element | Purpose | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Passage Length | Heat Exchange | Longer paths increase cooling efficiency |
| Material Choice | Thermal Conductivity | Use materials with high thermal mass |
| Air Flow Rate | Cooling Capacity | Balance between sufficient cooling and energy use |
| Moisture Control | Prevent Mold Growth | Implement proper drainage and ventilation |
Geothermal Heat Pumps
Geothermal heat pumps are the cornerstone of efficient home cooling systems that harness the Earth's stable underground temperature. These systems work by circulating a fluid through pipes buried in the ground, where it absorbs or releases heat depending on the season. In summer, the fluid absorbs heat from your home and transfers it to the cooler earth, effectively cooling your living space.
You'll find several benefits to using geothermal heat pumps:
- Energy efficiency: They use 25-50% less electricity than conventional HVAC systems
- Long lifespan: With proper maintenance, they can last up to 50 years
- Versatility: They can both heat and cool your home
- Environmentally friendly: They produce no direct emissions
While the initial installation cost can be high, you'll see significant savings on your energy bills over time.
It's important to take into account your property's size and soil composition when planning a geothermal system. You'll need enough land for the underground loop system, which can be installed horizontally or vertically depending on available space.
With proper design and installation, a geothermal heat pump can provide reliable, eco-friendly cooling for your home year-round.
Earth-Sheltered Home Construction

When considering earth-sheltered home construction, you'll need to address key design considerations to maximize geothermal cooling benefits.
You must prioritize proper insulation and waterproofing to prevent moisture issues and maintain temperature stability.
Guarantee adequate ventilation and lighting in your earth-sheltered home to create a comfortable living environment while harnessing the earth's natural cooling properties.
Design Considerations
Earth-sheltered home construction requires careful planning and design to maximize geothermal cooling benefits. When designing your earth-sheltered home, consider the local climate, soil conditions, and topography. These factors will influence the depth and orientation of your structure, as well as the insulation requirements.
To optimize geothermal cooling, focus on these key design considerations:
- Thermal mass: Incorporate thick walls and floors to absorb and store cool temperatures from the surrounding earth.
- Ventilation: Design natural airflow pathways to circulate cool air throughout the living spaces.
- Insulation: Use high-quality insulation materials to prevent heat gain from above-ground surfaces.
- Moisture control: Implement proper drainage and waterproofing systems to prevent dampness and mold growth.
You'll need to work closely with architects and engineers experienced in earth-sheltered construction to guarantee your home meets building codes and safety standards.
They'll help you determine the best layout for your living spaces, considering factors like natural light, emergency exits, and structural integrity.
Insulation and Waterproofing
For earth-sheltered homes, proper insulation and waterproofing are vital to maintain a comfortable living environment and protect the structure from moisture damage.
You'll need to use high-quality insulation materials with a high R-value, such as extruded polystyrene or polyurethane foam, to prevent heat transfer between the earth and your living space. Apply insulation to the roof, walls, and floor, paying special attention to areas where the structure meets the ground.
Waterproofing is essential to prevent moisture infiltration. Start with a robust waterproofing membrane, like rubberized asphalt or bentonite clay, applied to the exterior walls and roof. Verify all seams are properly sealed and protected.
Install a drainage system around the perimeter of your home to divert water away from the structure. This should include a French drain and gravel backfill to facilitate water movement.
Don't forget to address vapor barriers and moisture control within the living space. Use dehumidifiers and proper ventilation to manage indoor humidity levels.
Regular inspections and maintenance of your insulation and waterproofing systems will help ascertain their long-term effectiveness and protect your earth-sheltered home from potential moisture-related issues.
Ventilation and Lighting
Proper ventilation and lighting are essential aspects of earth-sheltered home construction. To guarantee a healthy and comfortable living environment, you'll need to implement effective ventilation strategies and maximize natural light.
Mechanical ventilation systems, such as heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) or energy recovery ventilators (ERVs), can help maintain air quality by exchanging stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air while conserving energy.
For lighting, consider incorporating light wells, skylights, and clerestory windows to bring natural light into your earth-sheltered home. These features not only reduce the need for artificial lighting but also create a more open and inviting atmosphere.
When designing your home's layout, prioritize rooms that require the most natural light, such as living areas and kitchens, by placing them near windows or light wells.
To optimize ventilation and lighting in your earth-sheltered home:
- Install operable windows for natural ventilation when weather permits
- Use reflective surfaces to distribute natural light throughout the interior
- Implement smart lighting systems to reduce energy consumption
- Consider passive solar design principles to maximize natural light and heat gain
Underground Thermal Mass Techniques
How can you harness the Earth's natural cooling power? Underground thermal mass techniques offer an effective solution. By utilizing the Earth's stable temperature below the frost line, you can create a natural cooling system for your home.
Start by excavating an area adjacent to your house's foundation. Install a network of pipes or tubes in this space, ensuring they're buried deep enough to benefit from the cooler underground temperatures. These pipes should be connected to your home's ventilation system. As warm air from your house circulates through these underground pipes, it cools naturally before re-entering your living space.
You can enhance this system by incorporating a heat exchanger. This device transfers heat from the warm indoor air to the cooler ground, further improving efficiency. For ideal results, consider using highly conductive materials like copper for your piping system.
Another approach is to build earth-bermed or partially underground structures. These designs naturally maintain cooler temperatures due to the surrounding soil's thermal mass.
You can also create underground rooms or cellars specifically for cooling purposes, providing a revitalizing retreat during hot summer days.
Geothermal Radiant Floor Cooling

Geothermal radiant floor cooling offers a cutting-edge approach to home temperature control. This system utilizes the earth's stable temperature to cool your home through a network of pipes installed beneath your floors. As cool water circulates through these pipes, it absorbs heat from your living space, effectively lowering the indoor temperature.
To implement geothermal radiant floor cooling, you'll need to install a ground-source heat pump and a series of underground loops. The system can be integrated with your existing HVAC setup or function independently.
Here are some key benefits of this cooling technique:
- Energy-efficient: Uses minimal electricity compared to traditional air conditioning
- Silent operation: No noisy compressors or fans
- Even cooling: Eliminates hot and cold spots throughout your home
- Versatile: Can be used for both cooling and heating
You'll find that geothermal radiant floor cooling is particularly effective in climates with moderate cooling needs. It's an ideal solution for maintaining a comfortable temperature without the need for forced air systems.
While the initial installation costs may be higher, you'll enjoy long-term energy savings and increased home comfort.
Earth-Air Heat Exchangers
Earth-air heat exchangers offer an innovative approach to home cooling.
You'll need to carefully plan the system's design and installation, considering factors like soil conditions, pipe depth, and airflow requirements.
While initial costs may be higher than traditional cooling methods, you can expect significant energy savings and reduced utility bills over time.
System Design and Installation
The heart of an effective earth-air heat exchanger lies in its careful design and proper installation. You'll need to evaluate factors like soil type, climate, and your home's layout to maximize efficiency.
Start by consulting a geothermal expert who can assess your property and recommend the best system configuration.
When designing your earth-air heat exchanger, pay attention to these key elements:
- Pipe material and diameter
- Depth and length of the underground network
- Air inlet and outlet locations
- Condensation management and drainage
For installation, you'll typically begin by excavating trenches or drilling boreholes to the required depth. The pipes are then laid and connected, ensuring proper slope for drainage.
It's essential to seal all joints and connections to prevent air leaks and water infiltration.
You'll also need to install air filters at the intake to maintain indoor air quality.
Finally, connect the system to your home's existing ductwork or install a dedicated air distribution system.
Efficiency and Cost Savings
Once your earth-air heat exchanger is properly designed and installed, you'll start reaping the benefits of this efficient cooling system.
Earth-air heat exchangers can greatly reduce your energy consumption and cooling costs. Depending on your climate and system design, you can expect to save 30-70% on your cooling bills compared to traditional air conditioning.
These systems are particularly effective in areas with high daily temperature fluctuations. During hot summer days, the cool earth temperature helps pre-cool incoming air, reducing the load on your AC unit.
In milder seasons, the system may completely eliminate the need for mechanical cooling.
The efficiency of your earth-air heat exchanger improves over time as the surrounding soil temperature stabilizes. You'll notice consistent performance year-round, with minimal maintenance required.
The system's longevity also contributes to its cost-effectiveness, with many components lasting 25-50 years.
To maximize savings, combine your earth-air heat exchanger with other energy-efficient practices like proper insulation and smart thermostat use.
Geothermal Cooling Towers

How do geothermal cooling towers fit into a home's cooling system? These structures work in tandem with your geothermal heat pump to dissipate excess heat from your home. Unlike traditional cooling towers used in large commercial buildings, residential geothermal cooling towers are smaller and more compact, designed to complement your home's aesthetics while providing efficient cooling.
Geothermal cooling towers offer several advantages for homeowners:
- Enhanced efficiency: They improve the overall performance of your geothermal system
- Reduced energy consumption: By optimizing heat rejection, they lower your cooling costs
- Environmentally friendly: They use less water and chemicals compared to conventional cooling methods
- Quiet operation: You'll enjoy a peaceful home environment with minimal noise disturbance
When installing a geothermal cooling tower, you'll need to take into account factors such as available space, local climate, and your home's cooling requirements.
It's essential to work with a qualified geothermal contractor who can properly size and integrate the cooling tower into your existing system.
While the initial investment may be higher than traditional cooling methods, the long-term energy savings and reduced environmental impact make geothermal cooling towers an attractive option for eco-conscious homeowners.
Borehole Thermal Energy Storage
Borehole Thermal Energy Storage (BTES) offers a unique approach to geothermal cooling for homes. This system uses deep, vertical boreholes drilled into the ground to store and extract thermal energy. You'll typically need multiple boreholes, each lined with a U-shaped pipe filled with a heat transfer fluid.
During cooler months, excess heat from your home is transferred to the ground through these pipes. The surrounding soil acts as a thermal battery, storing this energy for later use. When summer arrives, you can reverse the process, drawing the stored cool temperatures from the ground to cool your home.
BTES systems are highly efficient and can provide both heating and cooling. They're particularly effective in areas with significant temperature variations between seasons.
You'll need sufficient land area for the boreholes, which can be a limitation for some homeowners. The initial installation cost is higher than traditional cooling systems, but you'll see long-term energy savings and reduced carbon emissions.
Maintenance is minimal, and the system's lifespan can exceed 50 years. If you're looking for a sustainable, long-term cooling solution, BTES is worth considering.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does It Take to Recoup Costs of Installing Geothermal Cooling Systems?
You'll typically recoup costs for geothermal cooling systems within 5-10 years. However, the exact timeframe depends on factors like your energy usage, local utility rates, and the system's efficiency. It's a long-term investment in comfort and savings.
Can Geothermal Cooling Be Combined With Traditional Air Conditioning Systems?
Yes, you can combine geothermal cooling with traditional AC systems. It's called a hybrid system. You'll use geothermal for most cooling needs, but the AC kicks in during extreme heat. This setup maximizes efficiency and comfort.
What Maintenance Is Required for Geothermal Cooling Systems?
You'll need to regularly clean or replace air filters, inspect piping for leaks, and have a professional check the heat pump annually. Don't forget to maintain proper antifreeze levels and keep outdoor components clear of debris.
Are There Any Health Risks Associated With Geothermal Cooling Techniques?
You'll be pleased to know that geothermal cooling techniques generally don't pose significant health risks. They're safe and eco-friendly. However, you should guarantee proper installation and maintenance to prevent issues like mold growth or poor air quality.
How Do Local Building Codes and Regulations Affect Geothermal Cooling Installations?
You'll need to check local building codes and regulations before installing geothermal cooling. They can affect permitting, system design, and installation requirements. It's essential to comply with zoning laws and obtain necessary approvals to avoid legal issues.
In Summary
You've now explored 10 innovative geothermal cooling techniques for your home. By harnessing the Earth's stable temperature, you can create a naturally comfortable living space while reducing your energy costs and environmental impact. Whether you're building a new home or retrofitting an existing one, there's a geothermal solution that can work for you. Embrace these eco-friendly methods, and you'll enjoy sustainable cooling year-round. It's time to make the switch to geothermal comfort!





Leave a Reply