To assess your home's geothermal potential, start by evaluating your property's geology and soil conditions. Next, calculate your space heating requirements based on your home's size and insulation. Then, assess the available land area for installing ground loops. Consider your local climate conditions, as they'll impact system efficiency. Finally, consult with geothermal installation professionals for a thorough site assessment and cost estimates. These five steps will help you determine if geothermal energy is a viable option for your home. By exploring each step in detail, you'll gain a thorough understanding of your property's geothermal potential.
Evaluate Your Property's Geology
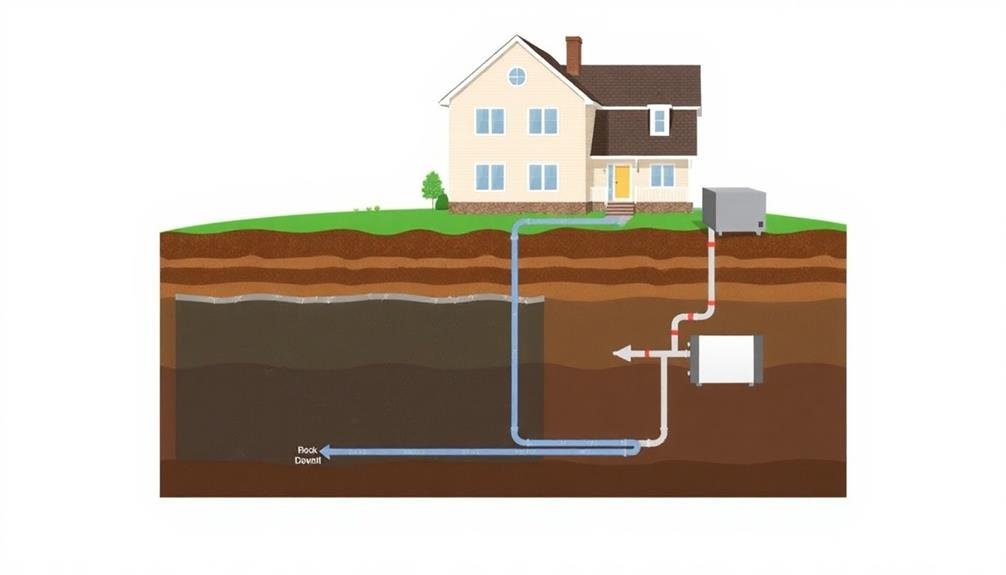
Before diving into geothermal installation, it's vital to assess your property's geological makeup. The type of soil and rock beneath your home greatly impacts the efficiency and feasibility of a geothermal system. Start by researching your area's geological maps, which are often available through local government offices or online databases. These maps can provide valuable insights into the underlying rock formations and soil types.
Next, consider hiring a professional geologist or geotechnical engineer to conduct a site-specific survey. They'll analyze soil samples, bedrock depth, and groundwater levels. This information is important for determining the most suitable type of geothermal system for your property. For instance, areas with high groundwater levels might be better suited for open-loop systems, while properties with stable bedrock could benefit from vertical closed-loop systems.
Pay attention to thermal conductivity, as it affects heat transfer efficiency. Soil with high moisture content generally conducts heat better than dry soil.
Also, consider your property's topography and available land area. Sloped terrain might require additional excavation, while limited space could necessitate vertical borehole systems instead of horizontal loops.
Calculate Space Heating Requirements
Accurate space heating calculations form the foundation of a successful geothermal system. To determine your home's heating requirements, you'll need to take into account several factors.
Start by measuring your home's total square footage, including all heated areas. Next, assess your home's insulation quality and identify any air leaks or drafts that could affect heat retention.
Calculate your home's heat loss by factoring in the climate zone you live in, the number and size of windows, and the overall thermal efficiency of your building envelope. You'll also want to take into account your family's comfort preferences and lifestyle habits that might impact heating needs.
Don't forget to account for any planned renovations or additions that could alter your heating requirements in the future. It's vital to be as precise as possible in these calculations, as undersizing or oversizing your geothermal system can lead to inefficiency and increased costs.
Once you've gathered this information, use an online heat loss calculator or consult with a professional HVAC technician to determine your home's exact heating load in BTUs (British Thermal Units). This figure will be essential in selecting the right size geothermal heat pump for your property.
Assess Available Land Area

After calculating your home's heating requirements, you'll need to evaluate the available land area for your geothermal system. The size of your property plays a significant role in determining the type and configuration of the ground loop system you can install.
For horizontal loop systems, you'll need approximately 1,500 to 3,000 square feet of open land per ton of heating and cooling capacity. This type of system is often the most cost-effective but requires the most land area.
If you have limited space, contemplate a vertical loop system. These systems require less surface area but involve drilling deeper into the ground, typically 100 to 400 feet.
Assess your property's layout, including any obstacles like trees, structures, or underground utilities. You'll also need to take into account local zoning regulations and setback requirements that may affect where you can install the system.
If you have a water source on your property, such as a pond or lake, you might be able to use a pond loop system. This option can be highly efficient and requires less land disturbance, but the water body must meet specific depth and volume requirements.
Determine Local Climate Conditions
Your local climate plays an essential role in evaluating your home's geothermal potential. To determine your area's climate conditions, start by researching average annual temperatures, seasonal variations, and extreme weather patterns.
You'll want to pay close attention to the ground temperature at various depths, as this directly affects the efficiency of a geothermal system. In colder climates, you'll need a deeper ground loop to access more stable temperatures, while warmer regions may require shallower installations.
Precipitation levels and soil moisture content also impact heat transfer rates, so consider your area's rainfall and groundwater patterns. Don't forget to account for potential future climate changes that could affect your system's long-term performance.
To gather this information, consult local weather stations, geological surveys, and climate databases. You can also reach out to nearby geothermal installers who may have specific data for your area.
Consult Geothermal Installation Professionals

Once you've gathered initial information about your local climate and geological conditions, it's crucial to consult with geothermal installation professionals.
These experts can provide valuable insights and conduct a thorough assessment of your property's geothermal potential. They'll evaluate factors like soil composition, groundwater levels, and available space for the system.
During your consultation, geothermal professionals will:
- Perform a site survey to determine the best location for the ground loop
- Calculate your home's heating and cooling loads
- Recommend the most suitable type of geothermal system for your needs
- Estimate installation costs and potential energy savings
- Explain local regulations and permit requirements
Don't hesitate to ask questions about their experience, certifications, and previous installations.
Request references and examples of similar projects they've completed. A reputable installer will be happy to provide this information and address any concerns you may have.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does a Geothermal System Typically Last?
Your geothermal system can last 20-25 years for indoor components and 50+ years for ground loops. You'll enjoy long-term reliability, but remember to maintain the heat pump regularly for peak performance throughout its lifespan.
Can Geothermal Energy Be Used for Cooling as Well as Heating?
Yes, you can use geothermal energy for cooling too. Your geothermal heat pump works in reverse during summer, extracting heat from your home and transferring it to the cooler ground. It's an efficient, year-round climate control solution.
What Are the Average Maintenance Costs for a Geothermal System?
You'll typically spend $200-$500 annually on maintenance for your geothermal system. It's lower than traditional HVAC systems. Costs include filter changes, occasional pump checks, and antifreeze top-ups. Every 20 years, you might need to replace the heat pump.
Are There Government Incentives or Tax Credits for Installing Geothermal Systems?
Yes, there are government incentives for geothermal systems. You'll find federal tax credits covering 30% of installation costs. Many states offer additional rebates or tax incentives. Check with your local energy office for specific programs available to you.
How Noisy Are Geothermal Heat Pumps Compared to Traditional HVAC Systems?
You'll find geothermal heat pumps are considerably quieter than traditional HVAC systems. They don't have outdoor units, so there's no noisy compressor outside. Inside, they operate at whisper-quiet levels, enhancing your home's comfort and tranquility.
In Summary
You've now got a solid grasp on how to evaluate your home's geothermal potential. By assessing your property's geology, calculating heating needs, evaluating land area, considering climate conditions, and consulting professionals, you're well-equipped to make an informed decision. Remember, geothermal energy can be a cost-effective, eco-friendly heating solution for many homes. Don't hesitate to reach out to experts for a detailed evaluation and to explore your options further.





Leave a Reply