Radiant floor heating offers efficient warmth through under-floor elements. You'll find three main types: electric, hydronic, and air-heated systems. Their efficiency depends on factors like insulation, flooring type, and climate. Typically, radiant heating is up to 30% more efficient than forced-air systems and ideal for allergy sufferers. To measure efficiency, look at metrics like Coefficient of Performance (COP) and R-value. Proper installation, quality components, and regular maintenance maximize performance. When comparing to traditional methods, radiant heating provides consistent warmth without circulating allergens. To access the full potential of your radiant floor heating system, there's much more to explore.
Understanding Radiant Floor Heating Systems
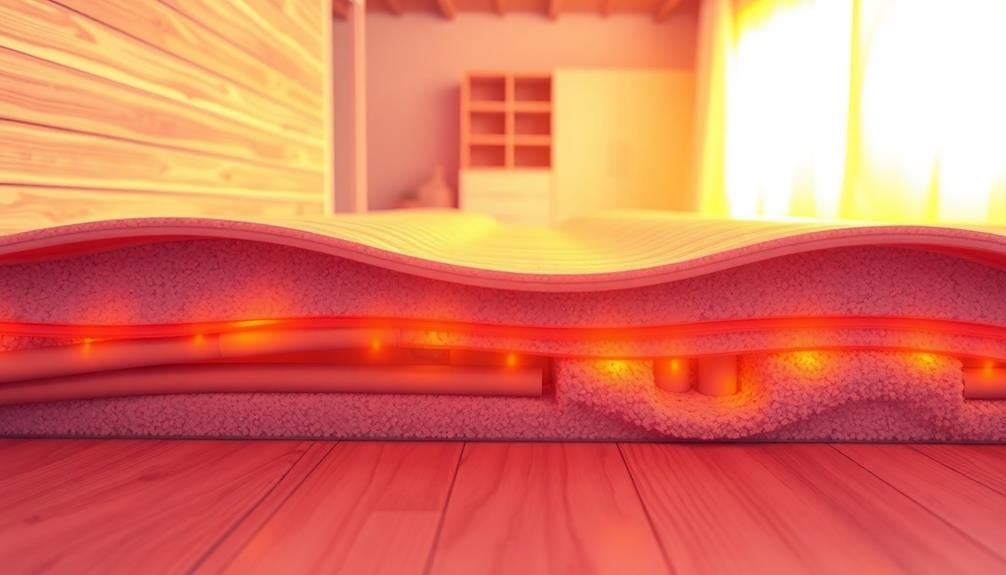

Radiant floor heating systems offer a cozy and efficient way to warm your home. These systems work by installing heating elements beneath your floor, which radiate heat upward through the surface. Unlike traditional forced-air systems, radiant heating provides consistent warmth from the ground up, eliminating cold spots and drafts.
There are three main types of radiant floor heating: electric, hydronic, and air-heated. Electric systems use cables or mats embedded in the floor, while hydronic systems circulate hot water through pipes. Air-heated systems, though less common, use warm air to heat the floor. Each type has its advantages, with electric being easier to install and hydronic generally more cost-effective for larger areas.
You'll find radiant heating compatible with various flooring materials, including tile, stone, hardwood, and even carpet. The system's efficiency depends on factors like insulation, floor covering, and climate.
When properly installed, radiant floor heating can be up to 30% more efficient than forced-air systems, as it doesn't lose heat through ductwork. It's also ideal for those with allergies, as it doesn't circulate dust and allergens.
Efficiency Ratings and Measurements
When you're considering radiant floor heating, understanding efficiency ratings and measurements is vital. The primary metric you'll encounter is the Coefficient of Performance (COP), which measures how efficiently the system converts energy into heat. A higher COP indicates better efficiency, with most quality systems achieving a COP between 3 and 4.
Another important factor is the R-value, which measures thermal resistance. For radiant floor heating, you'll want to guarantee proper insulation beneath the heating elements to minimize heat loss. The higher the R-value, the better the insulation.
You should also pay attention to the system's heat output, measured in BTUs (British Thermal Units) per square foot. This will help you determine if the system can adequately heat your space.
Energy Star ratings can guide you towards more efficient models, while the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating is vital for gas-powered systems. AFUE measures the percentage of fuel converted to heat over a year, with higher percentages indicating better efficiency.
Lastly, consider the system's response time and temperature consistency, as these factors contribute to overall comfort and energy usage.
Factors Affecting System Performance
The performance of your radiant floor heating system hinges on several key factors. Insulation plays an essential role, as proper floor and room insulation prevent heat loss and improve efficiency.
The type of flooring you choose also impacts performance; materials like tile and concrete conduct heat better than wood or carpet.
Your system's design and installation are equally important. Proper spacing of heating pipes or cables guarantees even heat distribution, while correctly sized boilers or heat sources optimize energy use.
The quality of components, including manifolds, thermostats, and pumps, affects overall system efficiency.
Water temperature management is critical for hydronic systems. Lower water temperatures generally lead to better efficiency but may require longer warm-up times.
The depth at which heating elements are installed affects response time and heat output.
Room characteristics, such as ceiling height and window placement, influence how effectively heat is distributed.
Regular maintenance, including bleeding air from hydronic systems and keeping components clean, helps maintain peak performance.
Comparing Different Heating Methods
In comparison with other heating methods, radiant floor heating offers unique advantages. Unlike forced-air systems, it doesn't blow dust or allergens around your home, making it ideal for those with respiratory issues.
Radiant heating also provides consistent warmth from the ground up, eliminating cold spots and drafts common with traditional heating methods.
When compared to baseboard heating, radiant floor systems don't take up wall space, giving you more freedom in furniture placement. They're also more energy-efficient, as they don't lose heat through ductwork.
Radiant heating typically operates at lower temperatures than forced-air systems, potentially reducing your energy bills.
However, it's important to evaluate the drawbacks. Radiant floor heating has a higher upfront cost and can be challenging to install in existing homes.
It also has a slower response time compared to forced-air systems. While radiators and baseboard heaters can quickly warm a room, radiant floors take longer to heat up and cool down.
Ultimately, your choice depends on your specific needs, budget, and home layout. Think about consulting with a heating professional to determine the best option for your situation.
Maximizing Energy Savings

Efficiency is key when it comes to maximizing energy savings with radiant floor heating. To get the most out of your system, you'll need to focus on proper insulation, smart thermostat usage, and regular maintenance.
Insulate your floors, walls, and ceiling to prevent heat loss and improve overall efficiency. This will allow your radiant heating system to work less, consuming less energy while maintaining comfort.
Invest in a programmable thermostat to enhance your heating schedule. You can set lower temperatures when you're away or sleeping, and have the system warm up just before you return or wake up. This smart approach can considerably reduce your energy consumption without sacrificing comfort.
To further maximize energy savings, consider these three key strategies:
- Zone your heating system to heat only occupied areas
- Use solar panels to power your radiant floor heating
- Implement a hydronic system with a high-efficiency boiler
Regular maintenance is essential for peak performance. Clean and inspect your system annually, checking for leaks or inefficiencies.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does It Take to Install a Radiant Floor Heating System?
You'll find that installing a radiant floor heating system typically takes 1-3 days for a small room, and up to a week for larger areas. It depends on your home's layout, flooring type, and system complexity.
Can Radiant Floor Heating Be Used With All Types of Flooring Materials?
You can use radiant floor heating with most flooring materials, but some work better than others. Ceramic tile, stone, and concrete are ideal, while wood and carpet may reduce efficiency. Always consult with a professional for specific recommendations.
What Maintenance Is Required for Radiant Floor Heating Systems?
You'll find radiant floor heating systems require minimal maintenance. Regularly check for leaks, bleed air from the system, and inspect valves. You should also have a professional perform annual inspections to guarantee peak performance and longevity.
Are Radiant Floor Heating Systems Safe for Homes With Pets and Children?
Yes, radiant floor heating systems are safe for homes with pets and children. You'll find they don't pose burn risks, don't circulate allergens, and don't have exposed hot surfaces. They're an excellent choice for family-friendly homes.
Can Radiant Floor Heating Be Retrofitted Into an Existing Home?
Yes, you can retrofit radiant floor heating into an existing home. It's more challenging than installing it during construction, but it's doable. You'll need to take into account your flooring type, available space, and budget before proceeding.
In Summary
You've now got a thorough understanding of radiant floor heating efficiency. Remember, it's not just about the system itself, but how well it's installed and maintained. By considering factors like insulation, flooring materials, and proper setup, you'll maximize your energy savings. Don't forget to compare it with other heating methods for your specific needs. With this knowledge, you're well-equipped to make informed decisions about your home's heating system.





Leave a Reply