Vertical axis turbines are wind energy devices that rotate around a vertical shaft, capturing wind from any direction. They're ideal for home energy due to their compact size and ability to operate in turbulent urban wind conditions. You'll find two main types: Savonius and Darrieus, each with unique benefits. These turbines are quieter and less visually intrusive than horizontal axis models, making them suitable for residential areas. They can generate electricity in lighter winds but are generally less efficient at higher speeds. While they offer advantages like simplified maintenance and versatility, they also come with some limitations. Understanding the full picture will help you decide if they're right for your home energy needs.
Vertical Axis Turbine Basics

At the heart of home energy innovation, vertical axis turbines offer a unique approach to harnessing wind power. Unlike their horizontal counterparts, these turbines rotate around a vertical shaft, allowing them to capture wind from any direction.
You'll find two main types: Savonius and Darrieus. Savonius turbines use cup-shaped blades to catch the wind, while Darrieus turbines have curved blades that generate lift.
These turbines are particularly well-suited for residential use due to their compact design and ability to operate in turbulent wind conditions. They're often quieter and less visually intrusive than horizontal axis turbines, making them more neighbor-friendly.
You can install them on rooftops or in your yard, depending on available space and local regulations.
Vertical axis turbines typically have a lower cut-in speed, meaning they can start generating electricity in lighter winds. However, they're generally less efficient than horizontal axis turbines at higher wind speeds.
When considering a vertical axis turbine for your home, you'll need to assess your local wind patterns, energy needs, and available space to determine if it's the right fit for your situation.
Types of Vertical Axis Turbines
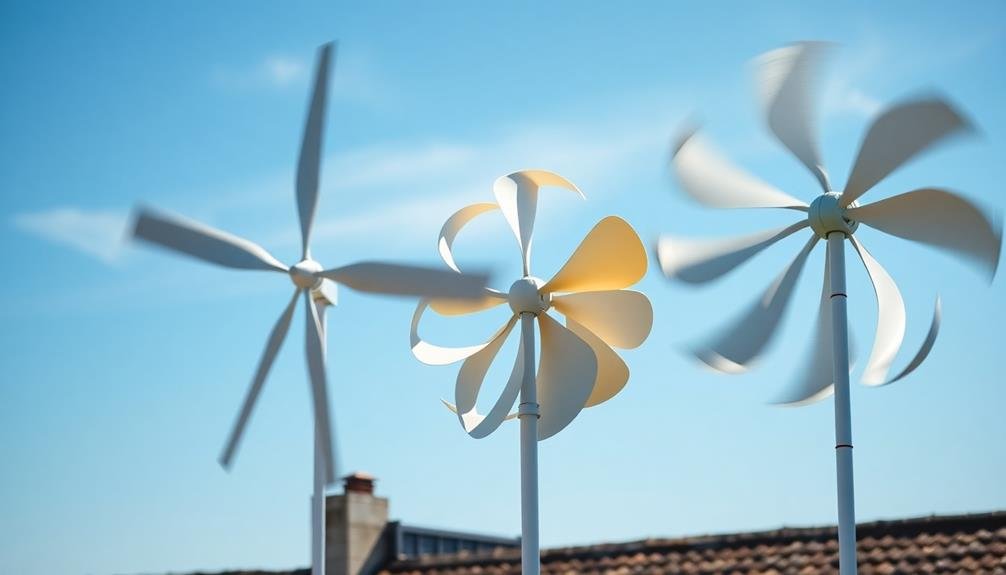

Several types of vertical axis turbines are available for home energy production, each with unique characteristics. The most common types you'll encounter are Darrieus, Savonius, and Giromill turbines.
Darrieus turbines, often called "eggbeater" turbines, have curved blades that resemble an elongated egg shape. They're efficient and can generate significant power, but they typically require a motor to start spinning.
Savonius turbines feature a simple S-shaped rotor design. They're less efficient than Darrieus turbines but can self-start in low wind speeds, making them ideal for urban environments.
Giromill turbines, also known as H-rotor turbines, have straight vertical blades attached to a central shaft. They combine features of both Darrieus and Savonius designs, offering a balance of efficiency and self-starting capability.
You'll also find hybrid designs that combine elements from different turbine types. For example, some turbines use a Savonius rotor at the center of a Darrieus design to improve self-starting ability.
When choosing a vertical axis turbine for your home, consider factors like wind conditions, available space, and local regulations to determine which type best suits your needs.
Advantages for Home Energy

Vertical axis turbines offer unique advantages for home energy production, making them an attractive option for homeowners.
They're more compact than traditional horizontal axis turbines, allowing for easier installation in residential areas with limited space. You'll find that these turbines can operate effectively in turbulent wind conditions, which are common in urban and suburban environments due to surrounding buildings and structures.
Another key advantage is their ability to capture wind from any direction without needing to reorient, unlike horizontal axis turbines. This means you'll get consistent energy production regardless of changing wind patterns.
Vertical axis turbines also tend to be quieter, reducing noise pollution concerns for you and your neighbors.
Maintenance is often simpler with vertical axis turbines, as their generator and gearbox are typically located at ground level. This makes repairs and routine checks more accessible and cost-effective.
Additionally, these turbines generally have a lower start-up speed, allowing you to generate electricity even in light wind conditions.
With their aesthetic design and smaller visual impact, vertical axis turbines can be more easily integrated into your home's architecture, potentially increasing property value while providing clean energy.
Disadvantages and Limitations

While vertical axis turbines offer numerous benefits, they also come with their share of drawbacks.
You'll find that these turbines generally have lower efficiency compared to their horizontal-axis counterparts. This means you'll generate less electricity from the same wind speed, potentially limiting your energy production.
You might encounter structural challenges too. Vertical axis turbines experience more turbulence and vibration, which can lead to increased wear and tear on components. This may result in higher maintenance costs and shorter lifespans for your turbine.
Another limitation you'll face is the need for a larger footprint. Vertical axis turbines often require more space than horizontal models with similar power outputs. This can be problematic if you have limited yard space or live in an urban area.
You should also be aware of potential noise issues. Some vertical axis designs can be noisier than horizontal turbines, which might be a concern if you live in a densely populated area or have close neighbors.
Lastly, you'll find fewer options available in the market for vertical axis turbines, potentially limiting your choices and increasing costs.
Installation Requirements

Despite these challenges, you'll find that vertical axis turbines can be relatively straightforward to install. You'll need a suitable location with unobstructed wind flow, typically on your roof or in an open area of your property. Confirm the structure can support the turbine's weight and withstand wind loads.
Before installation, check local zoning laws and obtain necessary permits. You may need to consult with a structural engineer to assess your roof's capacity. The turbine should be mounted on a sturdy pole or tower, usually 20-40 feet high, to capture ideal wind speeds.
You'll require an inverter to convert the turbine's DC output to AC for home use. Install a charge controller to regulate battery charging if you're using a battery storage system. Proper grounding and lightning protection are essential for safety.
Consider hiring a professional installer experienced with vertical axis turbines. They'll confirm proper wiring, connection to your home's electrical system, and compliance with local codes.
Regular maintenance, including checking for loose bolts, lubricating moving parts, and inspecting blades, will keep your turbine running efficiently for years to come.
Maintenance and Upkeep

Regular maintenance is vital for keeping your vertical axis turbine in top condition. You'll need to perform routine inspections of your turbine's components, including the blades, bearings, and generator. Check for any signs of wear, damage, or loose connections.
Clean the blades periodically to remove dirt, debris, or ice buildup, which can affect performance. Lubricate moving parts according to the manufacturer's recommendations, typically every 6-12 months. Pay special attention to the bearings, as they're critical for smooth operation.
Replace worn parts promptly to prevent further damage or reduced efficiency. Monitor your turbine's performance regularly. If you notice a decrease in energy output or unusual noises, investigate the cause immediately. You may need to adjust the blade pitch or balance to optimize efficiency.
Annually, have a professional inspect your turbine's electrical components, including the inverter and wiring. They'll guarantee everything's functioning correctly and compliant with local codes.
Keep detailed maintenance records, including dates of inspections, repairs, and part replacements. This information will help you track your turbine's performance over time and anticipate future maintenance needs.
Cost Considerations

After considering maintenance requirements, you'll want to examine the financial aspects of installing a vertical axis turbine. The initial cost can range from $2,000 to $10,000 for a small residential system, depending on size and power output. Larger or more advanced systems may cost considerably more.
You'll need to factor in installation expenses, which can add 20-30% to the turbine's price. Don't forget about permits and potential structural modifications to your property.
Over time, you'll incur ongoing costs for maintenance, repairs, and possible component replacements.
However, vertical axis turbines can lead to long-term savings on your electricity bills. The amount you'll save depends on your local wind conditions, energy consumption, and utility rates. Some areas offer incentives, tax credits, or rebates for renewable energy installations, which can offset your initial investment.
Consider the turbine's lifespan, typically 20-25 years, when calculating its overall cost-effectiveness. While the upfront costs may seem high, the long-term energy savings and potential increase in property value can make vertical axis turbines a worthwhile investment for your home energy needs.
Energy Output and Efficiency

The heart of any wind turbine system lies in its energy output and efficiency. When evaluating vertical axis turbines for home energy, you'll find that their energy production can vary greatly based on wind conditions and turbine design. Typically, these turbines generate between 1 to 10 kilowatts of power, which can cover a substantial portion of your household's energy needs.
Efficiency-wise, vertical axis turbines often perform better than horizontal axis models in turbulent wind conditions, common in urban and suburban areas. They can harness wind from any direction without needing to reorient, increasing their overall efficiency.
However, they generally have lower efficiency rates in steady, unidirectional winds compared to their horizontal counterparts.
You'll want to examine the turbine's cut-in speed, which is the minimum wind speed required to start generating electricity. Most vertical axis turbines have a lower cut-in speed, allowing them to produce power in lighter winds. This feature can be particularly advantageous if you live in an area with variable wind patterns.
To maximize your turbine's energy output, you'll need to carefully assess your location's wind resources and choose a model that's optimized for your specific conditions.
Noise and Environmental Impact

Many homeowners contemplating vertical axis turbines are concerned about their noise levels and environmental impact. You'll be pleased to know that these turbines are generally quieter than their horizontal-axis counterparts. The low-speed rotation and lack of gearboxes contribute to reduced noise pollution, making them more suitable for residential areas.
Environmentally, vertical axis turbines have several advantages. They're less likely to harm birds and bats due to their slower rotation and more visible blades. Additionally, they have a smaller visual impact on landscapes compared to large horizontal turbines.
Here's a comparison of environmental factors for different energy sources:
| Factor | Vertical Axis Turbines | Solar Panels | Fossil Fuels |
|---|---|---|---|
| Noise | Low | None | High |
| Wildlife Impact | Minimal | None | Significant |
| Visual Impact | Moderate | Low | High |
While vertical axis turbines do have some environmental impact, it's minimal compared to traditional energy sources. You'll need to weigh local regulations and zoning laws before installation, as some areas may have restrictions on turbine height or placement. Overall, these turbines offer a relatively eco-friendly option for home energy production.
Zoning and Permitting

Maneuvering the zoning and permitting process for vertical axis turbines can be challenging.
You'll need to check your local zoning laws to verify that wind turbines are allowed in your area. Many municipalities have height restrictions, setback requirements, and noise regulations that may affect your ability to install a turbine.
Before purchasing a vertical axis turbine, contact your local planning department to discuss your project. They'll guide you through the necessary steps and inform you of any required permits. You might need to submit a site plan, engineering drawings, and environmental impact assessments.
Some areas may require a special use permit or variance for wind turbines. This process often involves public hearings where neighbors can voice concerns. Be prepared to address issues like visual impact, noise, and property values.
If you live in a homeowners' association, you'll need to review their rules and potentially seek approval from the board. Some HOAs prohibit or restrict wind turbines.
Don't forget to check for any state or federal regulations that may apply to your project.
Some areas offer incentives for renewable energy installations, which could help offset the costs of permitting and installation.
Integrating With Existing Systems

Seamlessly integrating vertical axis turbines with your existing power systems is vital for maximizing their efficiency. You'll need to connect the turbine to your home's electrical grid through an inverter, which converts the turbine's DC output to AC power. This allows you to use the generated electricity directly or feed excess power back into the grid.
Consider installing a battery storage system to store surplus energy for use during low-wind periods. This setup enhances your energy independence and can serve as a backup power source during outages.
You'll also want to incorporate a charge controller to regulate the power flow and protect your batteries from overcharging.
Don't forget to update your home's electrical panel to accommodate the new power source. You may need to install a separate circuit breaker for the turbine system.
It's essential to integrate a monitoring system that tracks your turbine's performance and energy production. This data helps you optimize your energy usage and identify any maintenance needs.
Comparing to Horizontal Axis Turbines

When comparing vertical axis turbines to their horizontal counterparts for home energy, you'll need to evaluate several key factors.
You'll find differences in efficiency and power output, with horizontal axis turbines generally producing more energy in ideal wind conditions.
You'll also want to weigh the space requirements and noise levels, as vertical axis turbines often take up less room and operate more quietly, potentially reducing visual and auditory impact on your property.
Efficiency and Power Output
Typically, vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) are less efficient than their horizontal axis counterparts (HAWTs) when it comes to power output. VAWTs generally convert about 30-40% of wind energy into electricity, while HAWTs can achieve efficiencies of up to 50%. This difference is primarily due to the VAWT's design, which exposes only a portion of its blades to ideal wind conditions at any given time.
However, VAWTs have some advantages that can offset this efficiency gap. They're omnidirectional, meaning they don't need to reorient themselves to face the wind. This feature is particularly useful in urban environments with turbulent wind patterns. VAWTs also perform better in low wind speeds, which is often the case in residential areas.
When considering power output, you'll find that VAWTs typically generate less electricity than HAWTs of similar size. A small VAWT for home use might produce 1-4 kW, while a comparable HAWT could generate 2-10 kW.
However, VAWTs can be installed in tighter spaces and at lower heights, making them more suitable for residential applications where zoning restrictions or aesthetic concerns may limit HAWT installations.
Space Requirements
With respect to space requirements, vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) have a distinct advantage over horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWTs). VAWTs are more compact and can be installed in smaller areas, making them ideal for urban and suburban settings.
You'll find that their vertical design allows for a reduced footprint, often requiring less than half the space of a comparable HAWT.
VAWTs don't need to be oriented towards the wind, which means you can place them closer together without worrying about wake interference. This feature allows for higher power density in wind farms or residential installations.
Additionally, you won't need as much clearance around VAWTs, as they don't have large rotating blades that extend outward.
The compact nature of VAWTs also makes them easier to integrate into existing structures. You can mount them on rooftops, poles, or even incorporate them into building designs.
This versatility is particularly beneficial if you're dealing with limited land availability or zoning restrictions. Unlike HAWTs, which often require significant open space and may face height limitations, VAWTs can be a more practical solution for home energy production in densely populated areas.
Noise and Visual Impact
The compact design of vertical axis wind turbines doesn't just save space—it also contributes to reduced noise and visual impact compared to their horizontal axis counterparts.
You'll find that vertical axis turbines are generally quieter due to their slower rotation speeds and lower blade tip velocity. This means less aerodynamic noise, making them more suitable for residential areas where noise pollution is a concern.
Visually, vertical axis turbines have a sleeker, more modern appearance that many homeowners find less obtrusive than traditional windmills. Their smaller size and vertical orientation often blend better with urban and suburban landscapes, reducing the visual impact on your property and neighborhood.
When considering the aesthetic and auditory benefits of vertical axis turbines, you may experience:
- A sense of pride in your eco-friendly, design-conscious choice
- Relief from the worry of disturbing your neighbors with noise
- Satisfaction in maintaining your property's visual appeal
- Excitement about embracing cutting-edge renewable technology
Future of Residential Wind Energy

Looking ahead to the future of residential wind energy, we're likely to see significant advancements in vertical axis turbine technology. You'll witness improved efficiency, lower costs, and more aesthetically pleasing designs. Manufacturers will focus on developing turbines that can generate more power at lower wind speeds, making them suitable for a wider range of locations.
You can expect to see smart integration with home energy management systems, allowing for better optimization of power usage. This integration will help you maximize your energy savings and reduce reliance on the grid. Additionally, you'll find more compact and modular designs, making installation and maintenance easier for homeowners.
Here's a comparison of current and future vertical axis turbine features:
| Feature | Current | Future |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Moderate | High |
| Cost | High | Lower |
| Design | Bulky | Sleek |
| Smart Integration | Limited | Advanced |
As technology progresses, you'll see vertical axis turbines becoming a more viable option for residential renewable energy. They'll complement solar panels and energy storage systems, providing you with a thorough solution for your home's energy needs. With continued research and development, these turbines will play an important role in the shift to clean, sustainable energy for households worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Vertical Axis Turbines Be Used in Urban Environments With Tall Buildings?
Yes, you can use vertical axis turbines in urban environments with tall buildings. They're well-suited for these areas as they can capture wind from multiple directions and operate efficiently in turbulent airflow common around skyscrapers and other structures.
Are There Any Health Risks Associated With Living Near Vertical Axis Turbines?
You'll be pleased to know that there aren't significant health risks associated with living near vertical axis turbines. They're quieter than horizontal turbines and don't produce harmful emissions. However, some people report mild annoyance from low-frequency noise.
How Do Vertical Axis Turbines Perform in Extreme Weather Conditions Like Hurricanes?
You'll find that vertical axis turbines handle extreme weather well. They're designed to withstand high winds and can be easily lowered or secured during hurricanes. Their compact size and sturdy construction make them more resilient than traditional turbines.
Can Vertical Axis Turbines Be Painted or Customized to Blend With Home Aesthetics?
Yes, you can paint and customize vertical axis turbines to match your home's aesthetics. They're often available in various colors and finishes. You'll want to use weather-resistant paint and consult the manufacturer for specific recommendations.
Are There Any Government Incentives Specifically for Installing Vertical Axis Turbines?
You'll find most government incentives apply to all wind turbines, not just vertical axis types. Check your local and state programs for renewable energy rebates, tax credits, and grants that could help offset installation costs.
In Summary
You've learned about vertical axis turbines as an option for home energy. They've got some unique advantages but also face limitations. As you consider this technology, weigh the pros and cons carefully. Don't forget to check local regulations and your property's suitability. While they're not as common as horizontal axis turbines, vertical axis models could play a bigger role in residential wind energy's future. Keep an eye on evolving designs and efficiency improvements.




Leave a Reply